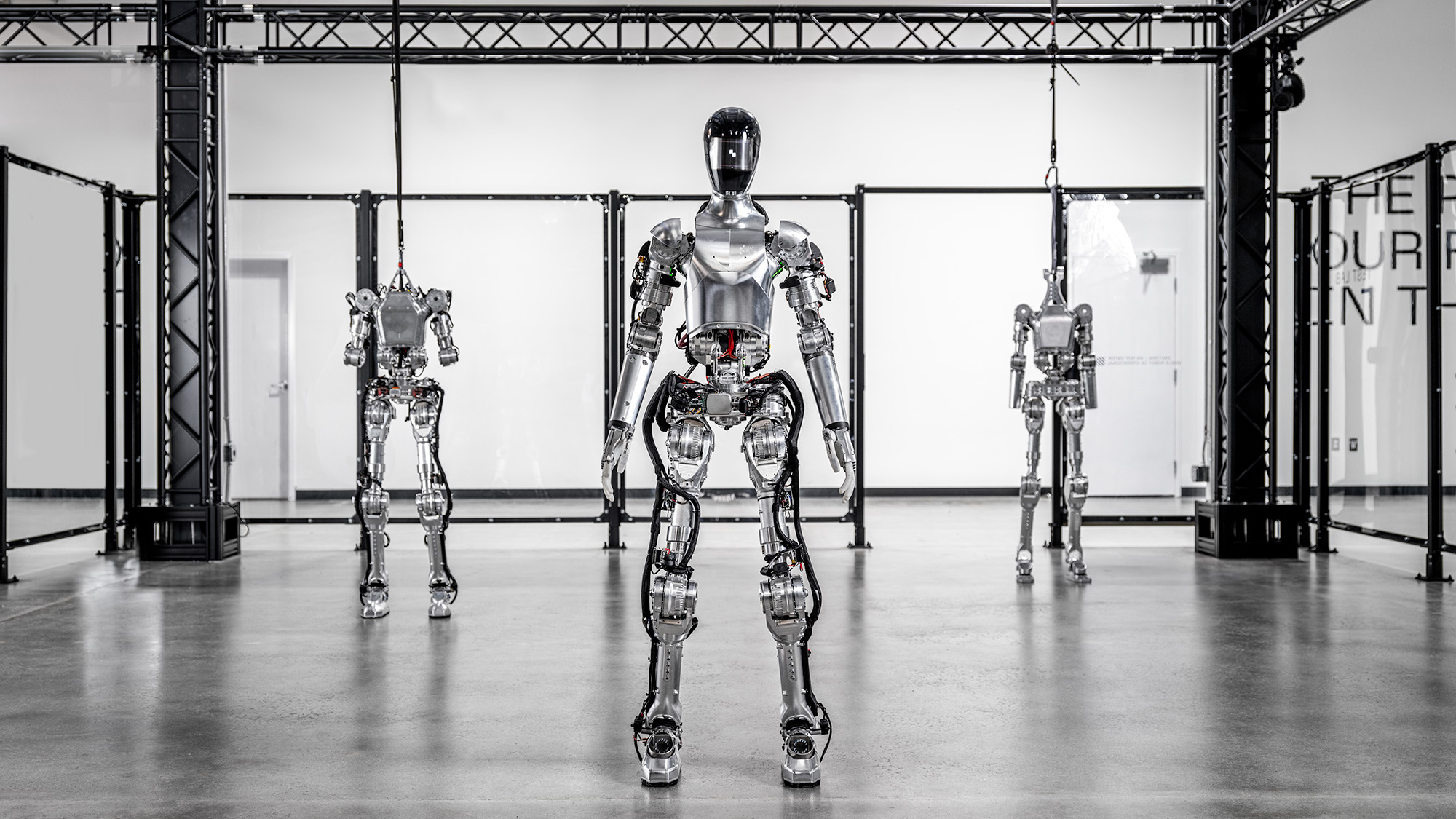
Microsoft has unveiled Rho-alpha, a groundbreaking Microsoft Physical AI model designed to significantly enhance robot performance beyond structured industrial environments. Derived from its Phi vision-language series, this strategic development addresses the critical need for robots to perceive, comprehend instructions, and dynamically adapt to real-world conditions. Consequently, Rho-alpha represents a calibrated leap towards more autonomous and versatile AI robot intelligence, moving beyond rigid, pre-scripted automation.
Architecting Dynamic Robotics: The Microsoft Physical AI Initiative
Traditional industrial robots operate efficiently within predictable parameters. However, Microsoft’s analysis indicates a performance gap in less structured, real-world scenarios. The core challenge lies in equipping robots with superior perception, instruction comprehension, and adaptability, rather than relying solely on fixed operational scripts. Rho-alpha, as Microsoft’s inaugural robotics model built on its Phi vision-language framework, is precisely positioned as a foundational step towards this vision of “physical AI.”
The Translation: Redefining Robot Autonomy
This initiative structurally shifts from static, programmed automation to dynamic, context-aware machine intelligence. Microsoft Physical AI, specifically Rho-alpha, integrates language, perception, and action into a unified model. This integration dramatically reduces dependence on predefined production lines and rigid instructions. Fundamentally, Rho-alpha translates natural language commands directly into precise robotic control signals, enabling robots to respond fluidly and autonomously to evolving tasks in diverse settings.
Socio-Economic Impact: Empowering Pakistan’s Workforce and Industry
How does this technological advancement influence the daily life of a Pakistani citizen? This development offers a robust “forward path” for national advancement. For students, it signifies burgeoning career opportunities in advanced robotics and AI development. Professionals in manufacturing and logistics can anticipate enhanced operational efficiencies, leading to higher productivity and potentially new industries. Households, particularly in urban centers, may benefit from optimized service delivery and supply chains. Ultimately, this structural shift paves the way for a more efficient and technologically advanced national infrastructure, creating high-skill jobs across urban and rural Pakistan.
The Forward Path: A Momentum Shift
This development undeniably represents a Momentum Shift. Microsoft’s Rho-alpha is a catalyst for genuine progress, moving beyond mere maintenance of existing capabilities. It provides a robust, scalable framework for robots to operate with unprecedented autonomy and intelligence, crucial for Pakistan’s integration into the global technological frontier.
Advancing Beyond Scripted Automation with Rho-alpha
Microsoft strategically links Rho-alpha to the broader paradigm shift toward physical AI. This new domain focuses on empowering software models to guide machines through environments that are inherently unstructured and not predefined. Consequently, the system’s unified approach to language, perception, and action minimizes reliance on fixed production lines and static instructions. Rho-alpha’s capability to translate natural language commands into direct robotic control signals enables robots to dynamically respond to complex tasks. A critical focus of the Rho-alpha model is bimanual manipulation, which mandates precise coordination between two robotic arms and fine-grained motor control. Microsoft affirms that Rho-alpha extends traditional vision-language-action approaches by broadening both its perception inputs and its learning sources.

Integrated Sensing: Vision, Touch, and Force Dynamics
Rho-alpha strategically incorporates tactile sensing alongside visual input, with additional sensing modalities, such as force, currently under rigorous development. These integrated capabilities are precisely engineered to help robots achieve a deeper understanding of physical interactions. This narrows the critical gap between simulated intelligence and nuanced real-world manipulation. Microsoft Research asserts these calibrated design choices aim to significantly improve how robots competently handle complex tasks in environments where conditions vary widely and cannot be fully anticipated in advance.

Catalyzing Training Through Simulation and Synthetic Data
A central tenet of Microsoft’s approach rigorously addresses the limited availability of extensive robotics data, particularly for tactile interactions. To overcome this systemic constraint, the company heavily leverages advanced simulation. Synthetic trajectories are precisely generated through reinforcement learning utilizing NVIDIA Isaac Sim. These are then strategically combined with physical demonstrations sourced from both commercial and open datasets. Deepu Talla, Vice President of Robotics and Edge AI at Nvidia, emphasized that training foundation models capable of complex reasoning and action necessitates overcoming the scarcity of diverse real-world data. He further underscored that deploying NVIDIA Isaac Sim on Azure allows Microsoft Research to accelerate the development of models like Rho-alpha, which are crucial for handling intricate manipulation tasks.

Human-in-the-Loop Learning: Calibrated Adaptation
Microsoft further emphasizes the pivotal role of human corrective input during operational deployment. Operators can intervene utilizing teleoperation devices and provide critical feedback, which the system can rigorously learn from over time. This establishes a robust training loop that expertly blends simulation data, real-world demonstrations, and precise human correction. This adaptive approach reflects a broader, strategic trend in robotics: leveraging advanced AI tools to systematically compensate for limited embodied datasets. Professor Abhishek Gupta, Assistant Professor at the University of Washington, observed that while teleoperated data collection is common, numerous environments render it impractical or impossible. He highlighted ongoing research collaboration with Microsoft Research to enrich pre-training datasets through diverse synthetic demonstrations, meticulously generated via simulation and reinforcement learning.